

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM April 2025 (REVISION 2817)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2817 (April 2025) is now available for download.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Numerical analysis of thermal response tests with groundwater flow and heat transfer model
This research, co-authored by J. Raymond, L. Gosselin, R. Lefebvre, and Aquanty’s René Therrien, explores how thermal response tests (TRTs) can be enhanced by employing HydroGeoSphere (HGS), our advanced modelling platform, to simulate coupled groundwater flow and heat transfer processes under complex geological settings. The study investigates the limitations of traditional line-source models, particularly in heterogeneous subsurface conditions, and introduces a numerical modelling approach to improve the accuracy of TRT analyses.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM March 2025 (REVISION 2796)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2796 (March 2025) is now available for download.

Using the debug.control file for real-time tuning of HGS simulation performance
This post explains how to use the debug.control file to modify the performance of an HGS simulation in real-time. By adjusting settings in the debug.control file, users can tweak parameters like convergence and time stepping without needing to restart the simulation. This is particularly helpful for optimizing the simulation's behavior during runtime. We find that using debug.control is a great way to test different settings and improve model performance on the fly. The file also provides the flexibility to pause simulations or adjust output, making it an essential tool for users looking to troubleshoot or fine-tune their models.
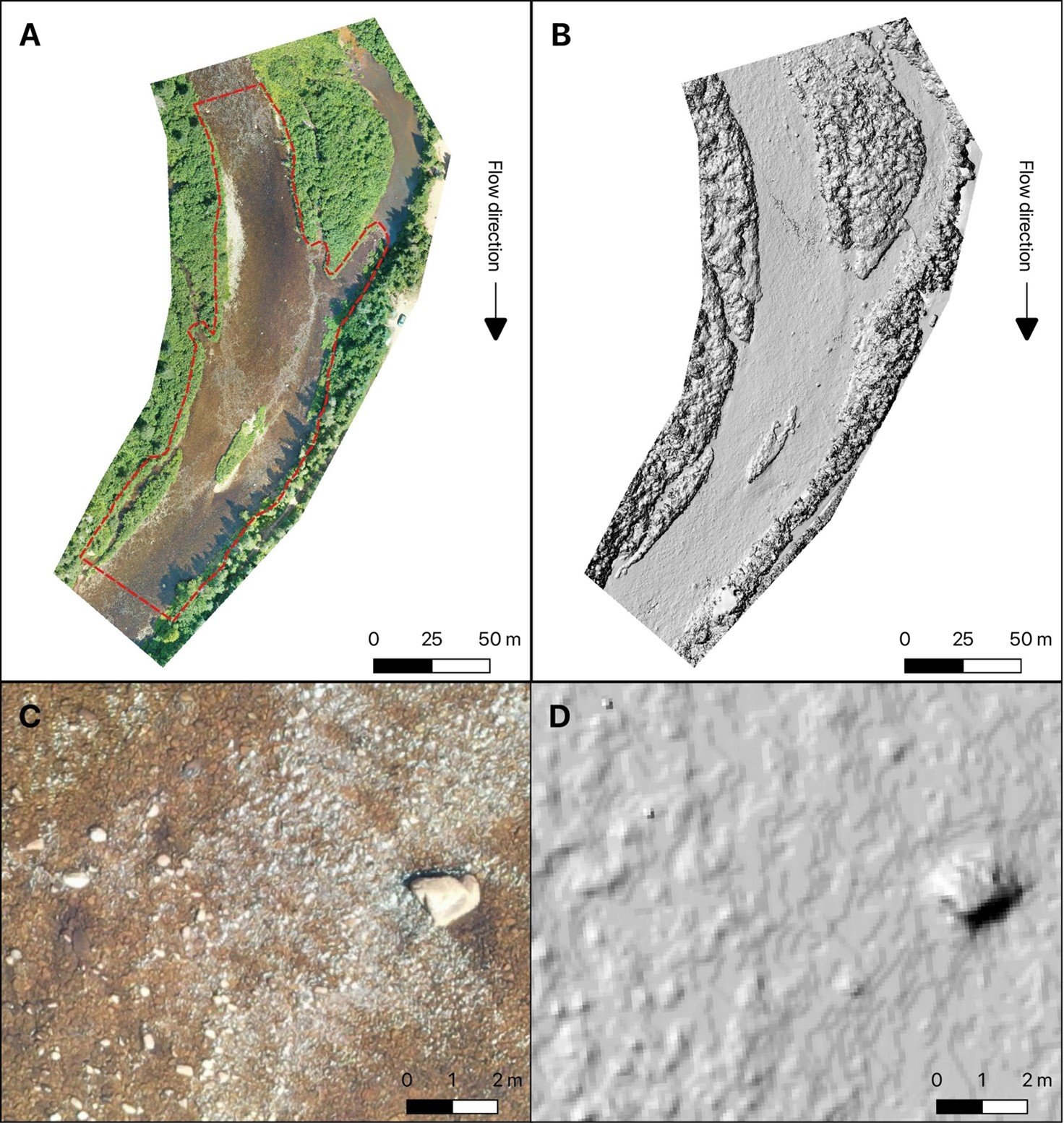
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – The HypoSalar project: Integrating hyporheic exchange fluxes into Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) spawning habitat models
In this research highlight ultra-fine resolution HydroGeoSphere models are used to simulate hyporheic exchange fluxes in river reaches used by Atlantic salmon for spawning. The HypoSalar project is contributing to demonstrate that the capabilities of HydroGeoSphere are not exclusively related to the field of hydrogeology, but can be used for both fluvial geomorphology and ecological studies due to HydroGeoSphere's flexibility and superior modeling approach.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM February 2025 (REVISION 2778)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2778 (February 2025) is now available for download.

Staff Research Highlight - Development of a fully integrated hydrological fate and transport model for plant protection products: incorporating groundwater, tile drainage, and runoff
This research investigates how the integrated hydrological modelling of plant protection products (PPPs) such as pesticides can provide a more comprehensive understanding of their environmental behavior across groundwater, surface water, and tile drainage systems.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM January 2025 (REVISION 2766)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2766 (January 2025) is now available for download.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM December 2024 (REVISION 2756)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2756 (December 2024) is now available for download.

HGS HIGHLIGHT – Estimating cumulative wastewater treatment plant discharge influences on acesulfame and Escherichia coli in a highly impacted watershed with a fully-integrated modelling approach
In this research highlight, researchers used HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to explore the impact of wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) discharge on surface water contamination in a mixed-use watershed in Ontario, Canada. The study focused on tracking acesulfame, a commonly used artificial sweetener, and Escherichia coli (E. coli), a fecal indicator, to understand how these contaminants move between surface and groundwater systems. Understanding the interactions between surface water and groundwater is critical in watersheds where WWTP discharge contributes to regional water quality concerns.
