
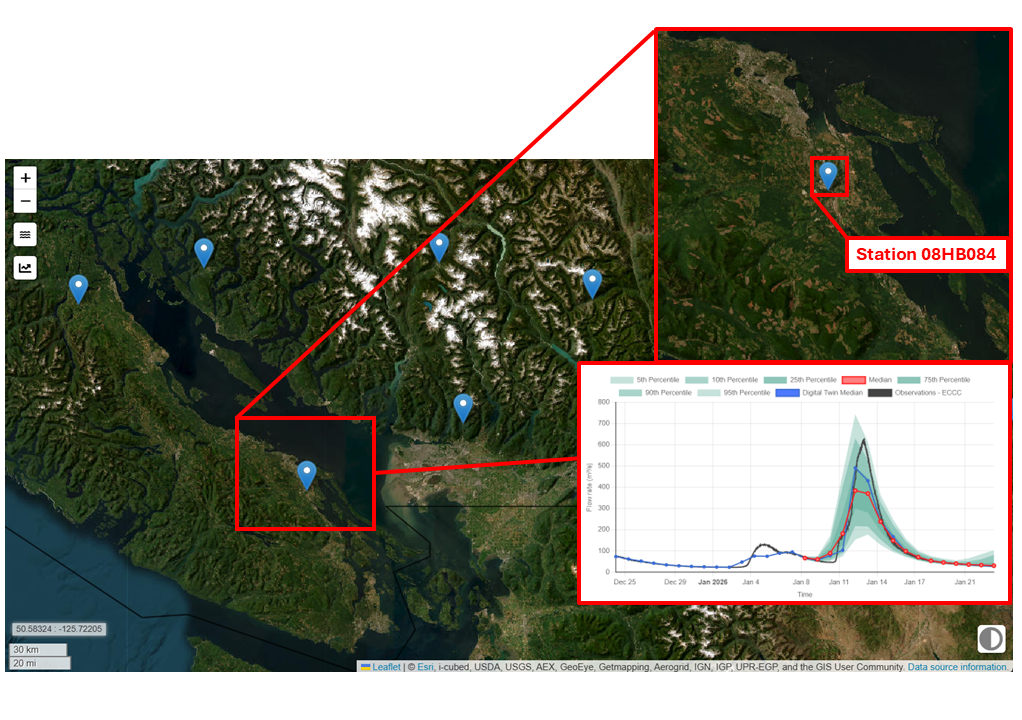
HydroSphereAI Case Study: Nanaimo River Near Cassidy – January 2026 High-Flow Event
On January 12, 2026, the Nanaimo River near Cassidy (Water Survey of Canada Station 08HB034) experienced a significant high-flow event, cresting at the 2-year flood mark. Winter storm systems sweeping across Vancouver Island brought prolonged precipitation to the watershed, driving river discharge well above average levels for the season. This case study highlights how an early release version of HydroSphereAI (HSAI) tracked the event and how this information could be used by stakeholders and water managers.
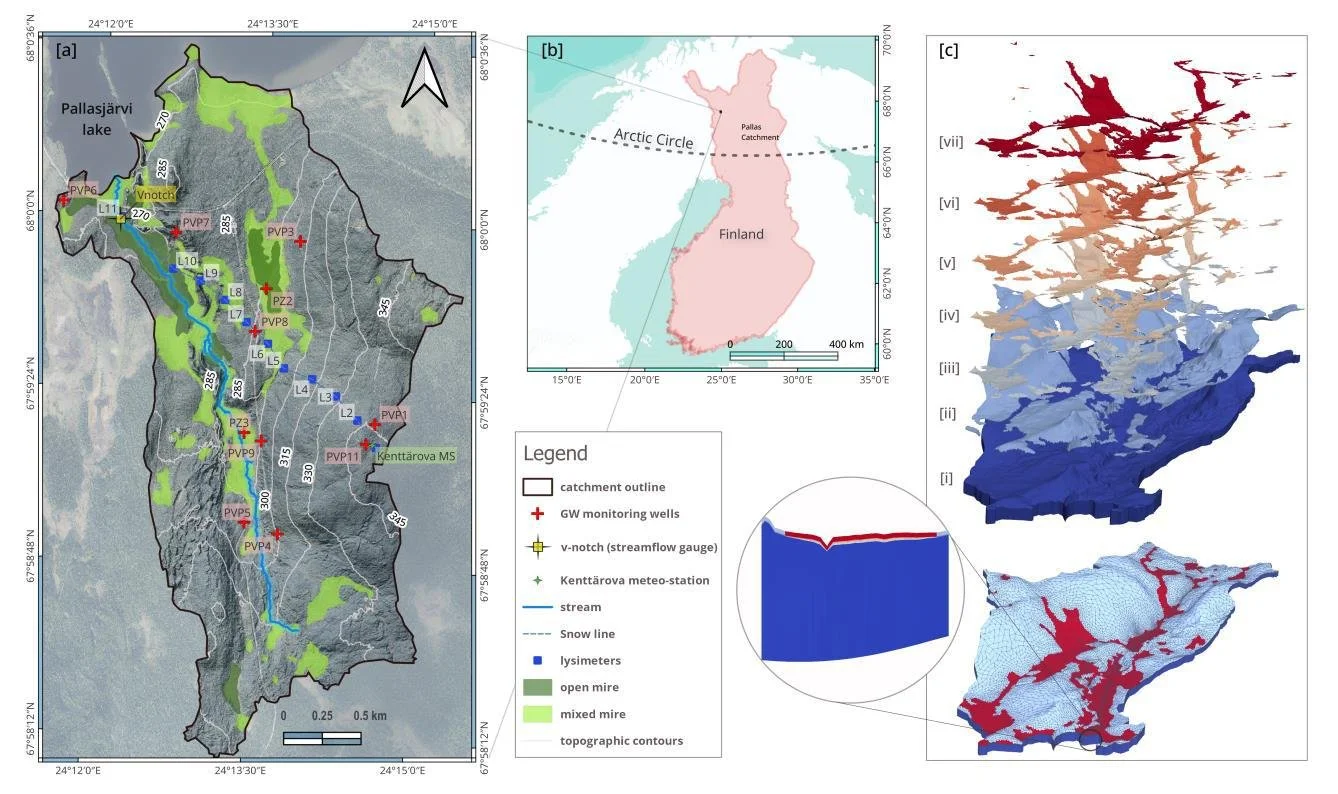
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Stable Water Isotopes Improve Calibration and Flow path Identification in Integrated Hydrological Model
This publication co-authored by Omar Ashraf Nimr, Hannu Marttila, Anna Autio, and Pertti Ala-Aho, investigates how stable water isotopes can improve calibration, uncertainty reduction, and flow path identification in fully integrated surface–subsurface hydrological models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to explicitly simulate both hydrologic processes and isotope transport, addressing long-standing challenges related to equifinality and internal process realism in groundwater–surface water modelling.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM March 2026 (REVISION 2928)
The HydroGeoSphere March 2026 release is now available for download.

Aquanty Featured in WaterPower Canada Guest Blog: Navigating Climate Change in Hydropower
We’re pleased to share that Aquanty recently contributed a guest blog post to WaterPower Canada, authored by Dr. Andre Erler, Senior Climate Scientist at Aquanty. The article “Harnessing Advanced Hydrologic Models to Help Canadian Hydroelectric Operators Navigate Climate Change” explores how advanced hydrologic modelling and forecasting tools can help Canadian hydroelectric operators navigate increasing uncertainty driven by climate change.
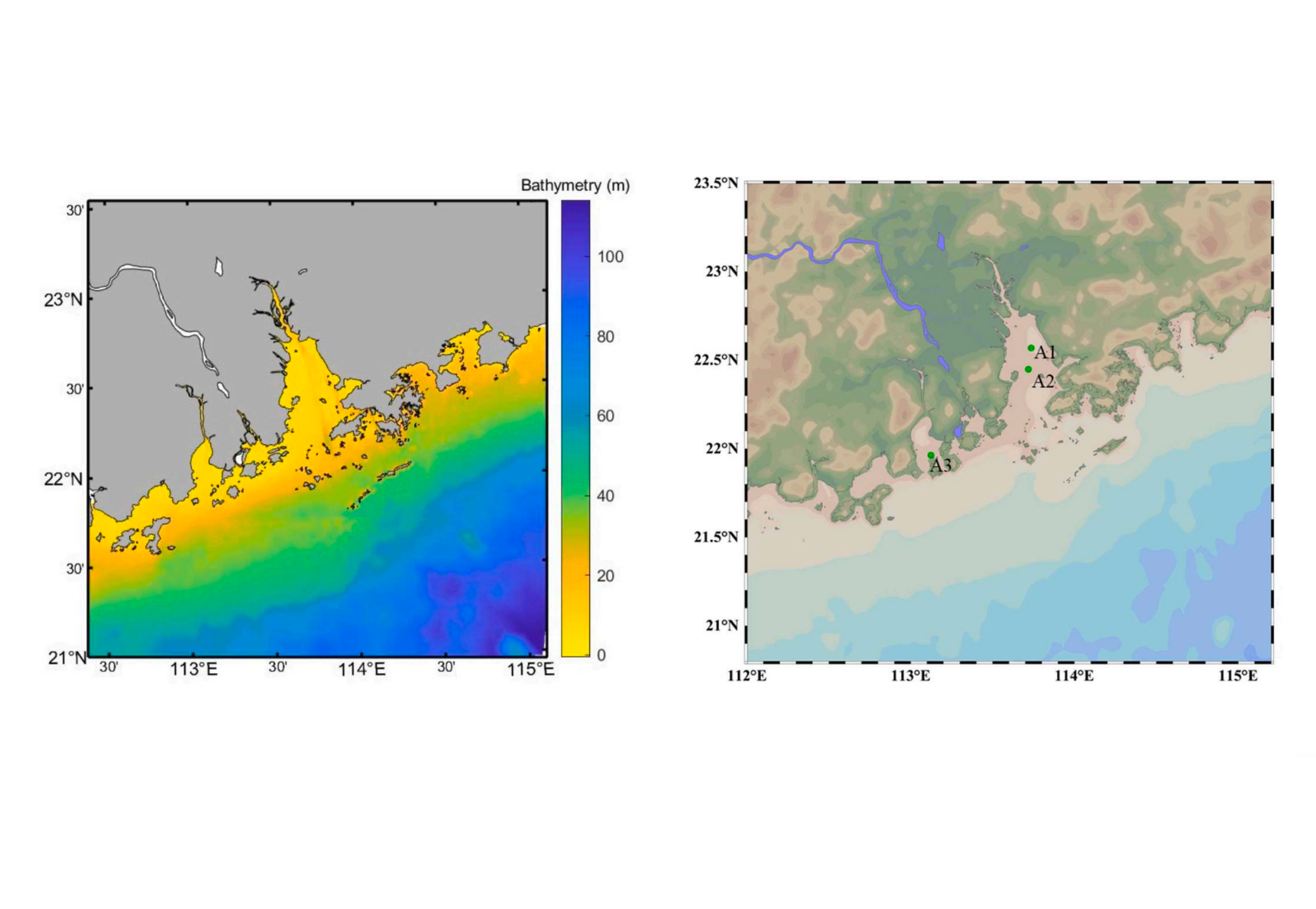
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Modeling the water use associated with energy consumption changes on saltwater intrusion in the Pearl River estuary, China
This research investigates how increased energy consumption and associated changes in water use impact saltwater intrusion in the Pearl River Estuary— one of China's most economically vital and environmentally vulnerable regions.
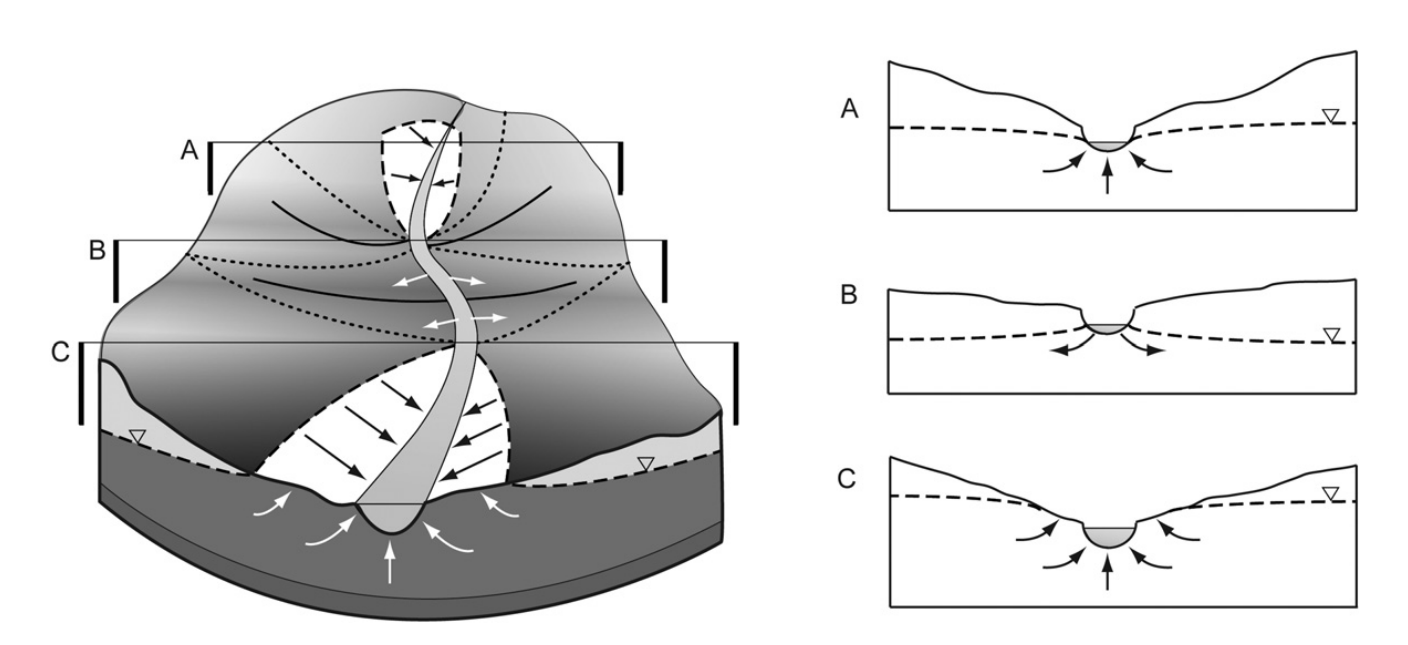
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – A hydraulic mixing-cell method to quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within spatially distributed fully integrated surface water–groundwater flow models
This research highlight co-authored by D. Partington, P. Brunner, C.T. Simmons, René Therrien, A.D. Werner, G.C. Dandy, and H.R. Maier, introduces a hydraulic mixing-cell (HMC) method to accurately quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within fully integrated surface–subsurface hydrologic models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to address long-standing challenges in decomposing streamflow generation mechanisms without relying on tracer transport simulations or simplifying assumptions about groundwater discharge.

HydroSphereAI Featured in Water Canada’s January/February 2026 Magazine
We’re excited to share that HydroSphereAI (HSAI) is featured in the January/February 2026 issue of Water Canada, highlighting how machine learning is helping close critical gaps in streamflow forecasting across Canada.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM February 2026 (REVISION 2918)
The HydroGeoSphere February 2026 release is now available for download.

HydroGeoSphere Development 2025: The Year in Review - Aquanty Webinar
We’re pleased to share the recording of our webinar ‘HydroGeoSphere Development 2025: The Year in Review’. This session, presented by Dr. Killian Miller, Numerical Analysis Specialist at Aquanty, looks back at a year of major advancements to the HydroGeoSphere platform— highlighting new features, performance improvements, and key structural updates across the HGS ecosystem.
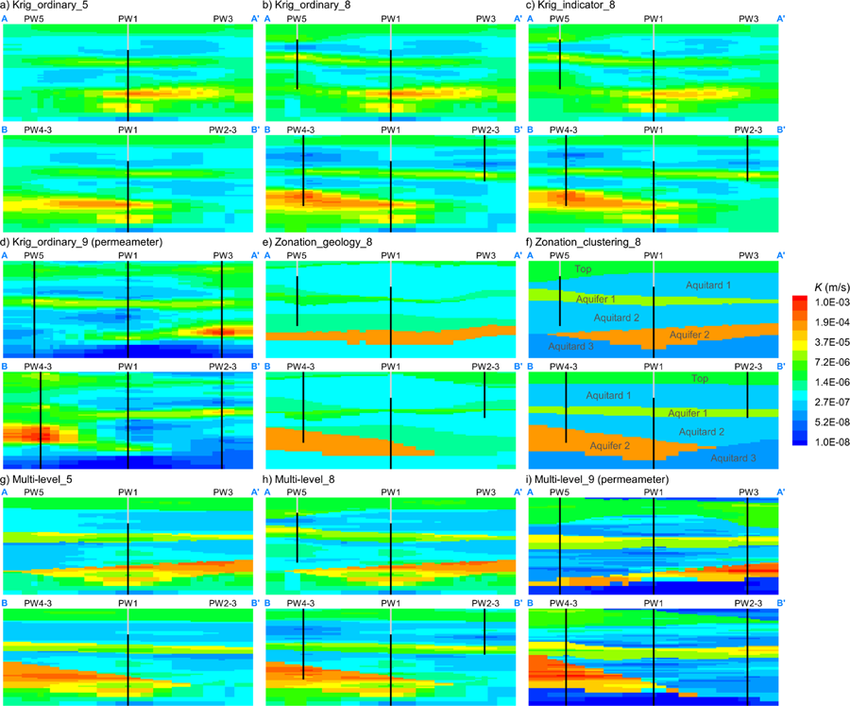
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Characterizing Spatial Heterogeneity of Hydraulic Conductivity Using Borehole NMR in a Complex Groundwater Flow System
This research highlight co-authored by Chenxi Wang, Colby M. Steelman, and Walter A. Illman, investigates how borehole nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging can be used to characterize subsurface heterogeneity and improve the representation of hydraulic conductivity in groundwater flow models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to evaluate the predictive performance of NMR-derived hydraulic conductivity (K) models and assess how different spatial interpolation and upscaling approaches influence flow and drawdown predictions in a highly heterogeneous aquifer system.
