

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Monetizing the role of water in sustaining watershed ecosystem services using a fully integrated subsurface–surface water model
This research, co-authored by David R. Lapen, Susan Preston, Tariq Aziz, and Steven K. Frey, highlights the role of subsurface water in sustaining ecosystem services during droughts. Using HydroGeoSphere (HGS), the team analyzed the South Nation Watershed (SNW) in eastern Ontario, emphasizing how subsurface water supports evapotranspiration in agricultural landscapes.

The Impact of SW-GW flow interactions for regional scale simulation of hydraulic heads: application in the south Quebec regional hydro system - Aquanty Webinar
A recording of our November 19th, 2024 webinar is now released.
This insightful session unpacks how the interplay between surface water (SW) and groundwater (GW) influences the accuracy of hydraulic head simulations in Southern Quebec, a region with significant water management challenges.

Assessing Groundwater and Surface Water Contributions to Evapotranspiration in a Semi-Arid Watershed - Aquanty Webinar
A recording of our October 30th, 2024 webinar is now released.
This session delves into how groundwater (GWET) and surface water (SWET) shape actual evapotranspiration (AET) dynamics in the North Saskatchewan River Basin— a vital area for understanding water balance in semi-arid regions.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Same soil, different climate: Crop model intercomparison on translocated lysimeters
In this research highlight, researchers explored the dynamics of crop modelling across diverse climatic conditions using translocated lysimeters. The study investigates how crop models perform when applied to the same soil under different climatic regimes, shedding light on the complex interplay between soil and crop dynamics amidst changing environmental conditions.
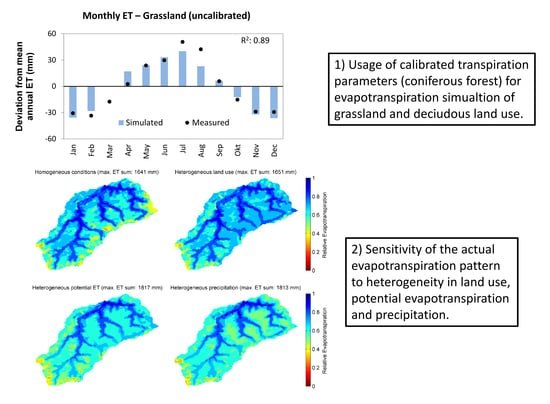
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Using High-Resolution Data to Test Parameter Sensitivity of the Distributed Hydrological Model HydroGeoSphere
By integrating HydroGeoSphere in this study, the researchers demonstrate its versatility in accommodating high-resolution data and conducting sensitivity analyses across different spatial scales. Precipitation emerges as the most sensitive input data, significantly influencing total runoff and peak flow rates. Additionally, the study highlights the importance of spatially distributed land use parameterization in accurately simulating evapotranspiration components and patterns.
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Simulating the recession dynamics of Arctic catchments in the context of a thawing permafrost
In a recent study, researchers have made significant strides in understanding how climate warming is altering the Arctic's hydrological dynamics. The study delves into the complex relationship between permafrost thaw and groundwater flow. Traditionally, Arctic hydrology has been conceptualized as a local system, confined by the frozen ground. However, as the climate warms, permafrost begins to thaw, transitioning this system into a more interconnected network of regional aquifers. This transformation is crucial, as it alters the fundamental dynamics of water movement and storage in the Arctic.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Understanding the vulnerability of surface–groundwater interactions to climate change: insights from a Bavarian Forest headwater catchment
This study used HydroGeoSphere to evaluate the impact of climate change on streamflow and water availability within a small forested catchment in South-East Germany. Climate forecasts in the region predict a significant decrease in precipitation over the coming decades. Based on integrated hydrologic modelling of the catchment, this forecasted decline in precipitation combined with a relatively steady rate of evapotranspiration (compared to the historical period) will result in prolonged drought conditions, which in turn will result in declining groundwater levels, decreased baseflow to the upstream reaches of the stream network.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Managing climate change impacts on the Western Mountain Aquifer: Implications for Mediterranean karst groundwater resources
A new study investigates the impact of climate change on water availability within a 9000 sqkm karstic aquifer in Israel and the West Bank, and couples HydroGeoSphere to a soil-epikarst water balance model.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Effect of topographic slope on the export of nitrate in humid catchments: a 3D model study
Agricultural nutrient runoff refers to the movement of excess nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, from agricultural lands into water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. While nutrients are essential for plant growth, excessive runoff can have significant impacts on both human and ecosystem health.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Evaluating Climate Change Impacts on Soil Moisture and Groundwater Resources Within a Lake-Affected Region
This study investigates how climate change could impact groundwater and soil moisture within the Great Lakes Basin (GLB). Groundwater is a resource that is relied on for agriculture, industry, municipalities, and drinking water. Approximately one-quarter of the 33 million inhabitants of the GLB depend on groundwater as their primary freshwater source. Given its extreme value as a natural resource, the impacts of climate change on groundwater need to be well understood, and fully-integrated models that incorporate such large water bodies (let alone an entire basin-scale system) are rare.
