
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – A hydraulic mixing-cell method to quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within spatially distributed fully integrated surface water–groundwater flow models
This research highlight co-authored by D. Partington, P. Brunner, C.T. Simmons, René Therrien, A.D. Werner, G.C. Dandy, and H.R. Maier, introduces a hydraulic mixing-cell (HMC) method to accurately quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within fully integrated surface–subsurface hydrologic models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to address long-standing challenges in decomposing streamflow generation mechanisms without relying on tracer transport simulations or simplifying assumptions about groundwater discharge.
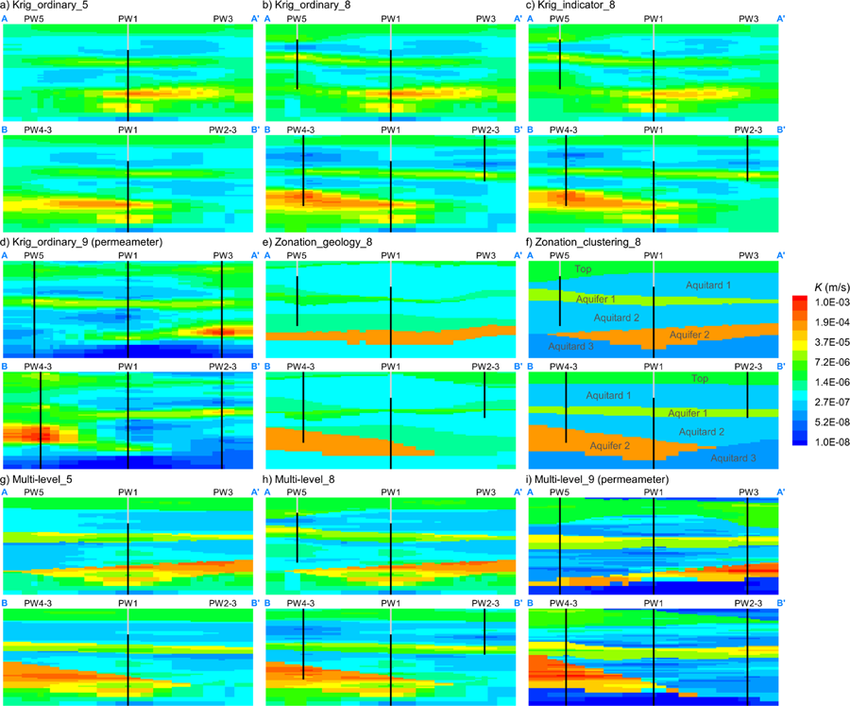
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Characterizing Spatial Heterogeneity of Hydraulic Conductivity Using Borehole NMR in a Complex Groundwater Flow System
This research highlight co-authored by Chenxi Wang, Colby M. Steelman, and Walter A. Illman, investigates how borehole nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging can be used to characterize subsurface heterogeneity and improve the representation of hydraulic conductivity in groundwater flow models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to evaluate the predictive performance of NMR-derived hydraulic conductivity (K) models and assess how different spatial interpolation and upscaling approaches influence flow and drawdown predictions in a highly heterogeneous aquifer system.

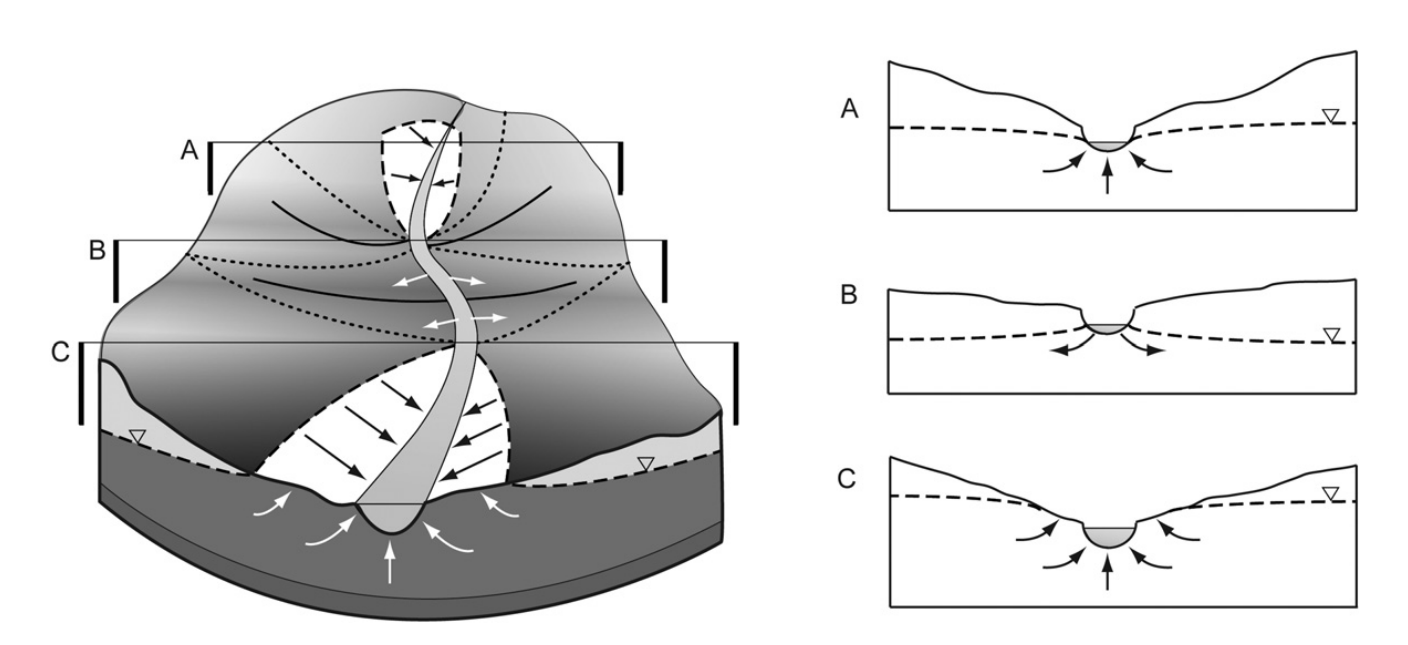
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Groundwater flow and age in topography-driven groundwater flow systems with geological barriers
The research examines how groundwater age and flow systems are influenced by topography and geological barriers, using numerical simulations to clarify the interaction between surface-driven flow and subsurface heterogeneity. Traditional models of topography-driven flow often assume homogeneous geologic conditions, which can obscure the role of stratigraphic variations in shaping groundwater movement and age distribution. This study offers a detailed exploration of how structural barriers— such as low-permeability formations— interrupt or redirect groundwater pathways and affect the spatial and temporal distribution of groundwater age.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – External and internal drivers behind the formation, vegetation succession, and carbon balance of a subarctic fen margin
In this research publication, researchers investigated the formation, vegetation succession, and carbon balance of peatland margins in Finnish Lapland. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) alongside paleoecological records and remote sensing to address long-standing challenges in understanding how new peatland areas initiate, expand, and influence climate through carbon cycling.

Staff Research Highlight - Improving precision in regional scale numerical simulations of groundwater flow into underground openings
The study presents a novel numerical framework to improve the accuracy of regional-scale groundwater flow simulations into underground openings, such as tunnels and deep geological repositories. Traditionally, simulating groundwater inflows into engineered underground structures has involved significant simplifications, often treating tunnels as drain features or imposing boundary conditions that fail to fully capture the physical behavior of fluid flow around these voids. This research addresses those limitations by introducing a new numerical boundary condition to simulate groundwater flow into underground openings more accurately.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Is the Water Balance of Your Waste Rock Pile Reliable? A framework for Improving Assessment of Water Inputs and Outputs for a Typical Storage Facility
This research focuses on understanding the dynamics of topography-driven groundwater flow systems using fully-coupled surface–subsurface hydrologic modelling. This study addresses long-standing challenges in representing nested flow systems by simulating interactions between climate, topography, and groundwater without relying on potentially unrealistic, static boundary conditions.

Staff Research Highlight - Understanding topography-driven groundwater flow using fully-coupled surface-water and groundwater modeling
This research focuses on understanding the dynamics of topography-driven groundwater flow systems using fully-coupled surface–subsurface hydrologic modelling. This study addresses long-standing challenges in representing nested flow systems by simulating interactions between climate, topography, and groundwater without relying on potentially unrealistic, static boundary conditions.
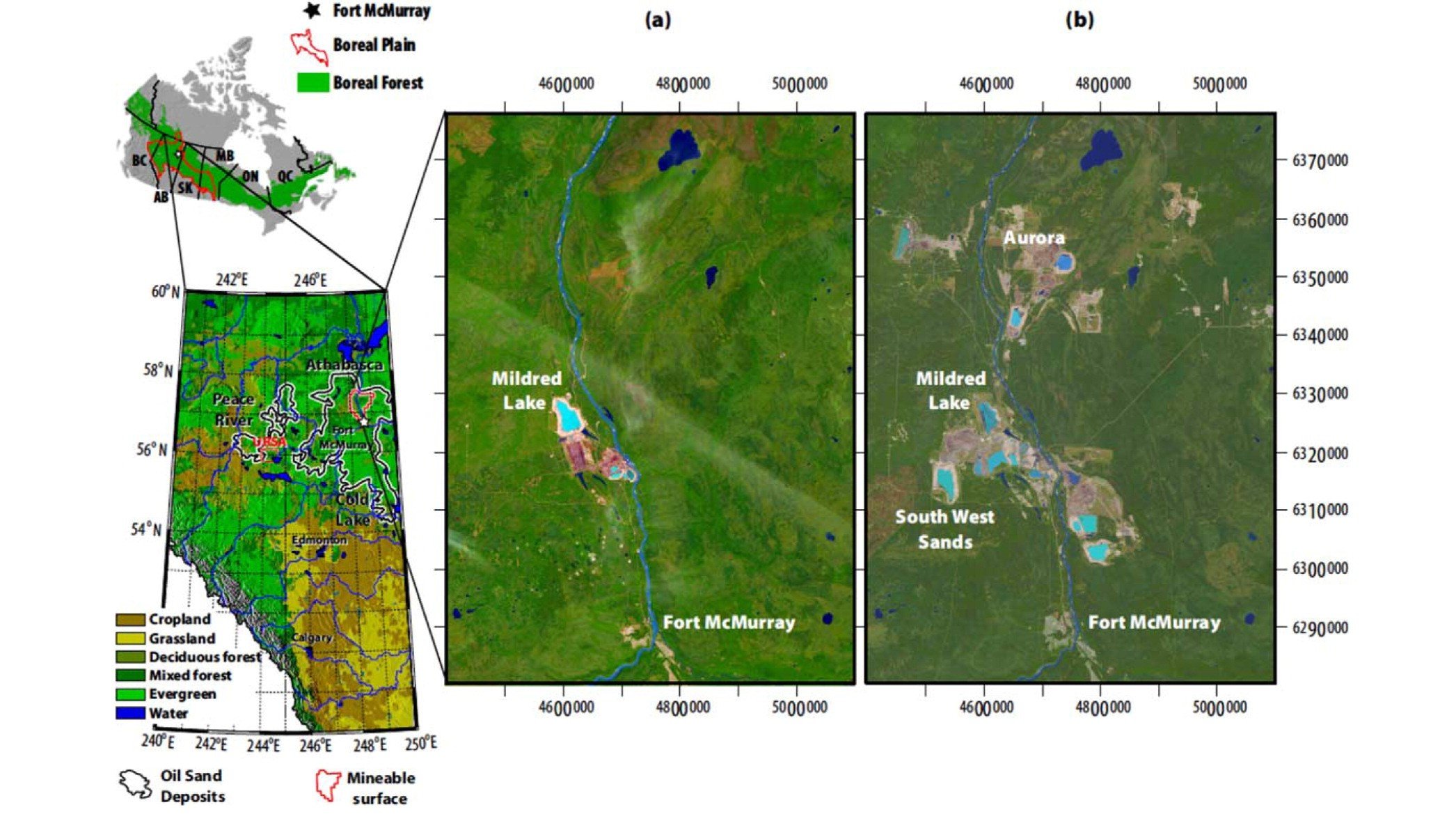
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Reclamation for aspen revegetation in the Athabasca oil sands: Understanding soil water dynamics
We’re pleased to highlight this publication which focuses on understanding soil water dynamics in reclaimed landscapes within the Athabasca oil sands region using unsaturated flow modeling. The study explores how different reclamation strategies affect soil water availability and water table fluxes— critical components for supporting aspen revegetation, a key species in boreal forest ecosystems.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Analyzing variation of the water table level with three-dimensional numerical simulations to assess reclamation techniques for an acidic tailings impoundment
As an extension of the last HGS research highlight titled ‘Improving control of contamination from waste rock piles’, this next research highlight within this series looks at a study conducted by the same researchers and explores the effects of thin cover deposition on managing water table levels in acidic tailings impoundments, while utilizing HydroGeoSphere (HGS) for in-depth simulations.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Improving control of contamination from waste rock piles
This study conducted by researchers investigates how well compacted cover layers on waste rock piles can mitigate infiltration into these waste piles, reducing the overall potential for oxidation of sulfidic waste materials and control environmental contamination. The research provides a detailed examination of how different cover configurations and hydrogeological conditions affect the performance of these covers in mitigating risks associated with waste rock piles.
