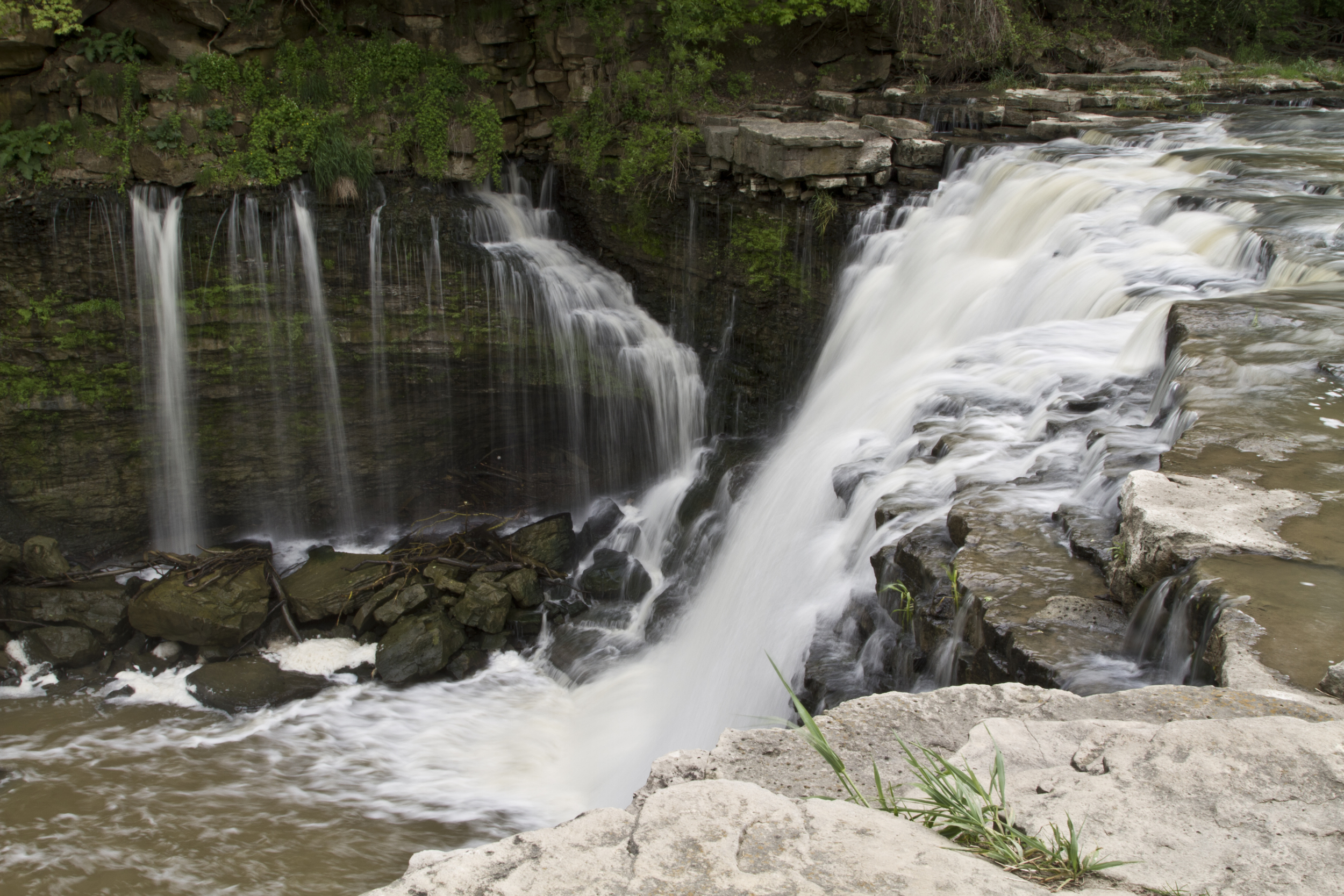

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – A hydraulic mixing-cell method to quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within spatially distributed fully integrated surface water–groundwater flow models
This research highlight co-authored by D. Partington, P. Brunner, C.T. Simmons, René Therrien, A.D. Werner, G.C. Dandy, and H.R. Maier, introduces a hydraulic mixing-cell (HMC) method to accurately quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within fully integrated surface–subsurface hydrologic models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to address long-standing challenges in decomposing streamflow generation mechanisms without relying on tracer transport simulations or simplifying assumptions about groundwater discharge.
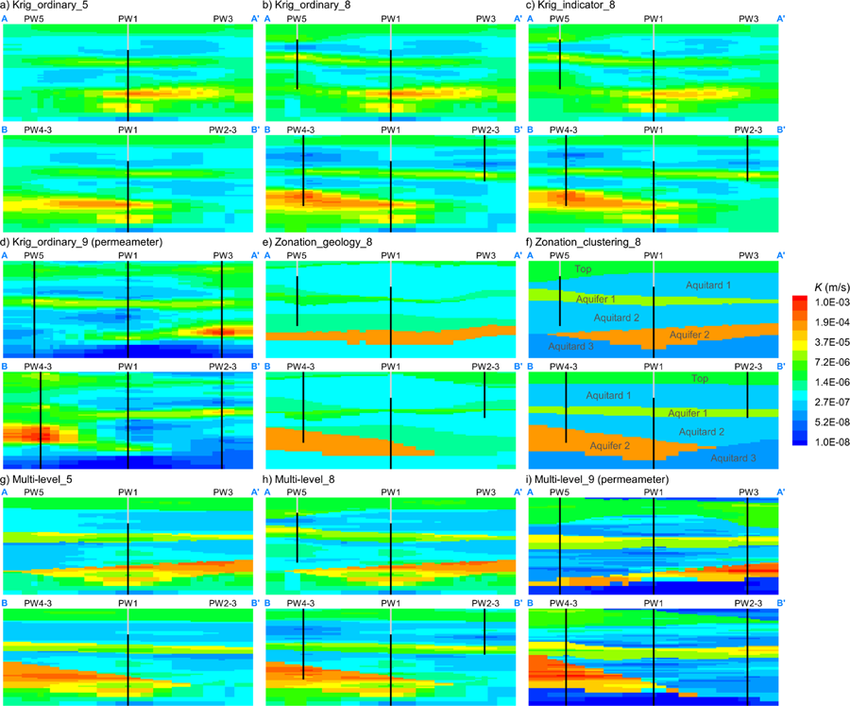
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Characterizing Spatial Heterogeneity of Hydraulic Conductivity Using Borehole NMR in a Complex Groundwater Flow System
This research highlight co-authored by Chenxi Wang, Colby M. Steelman, and Walter A. Illman, investigates how borehole nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging can be used to characterize subsurface heterogeneity and improve the representation of hydraulic conductivity in groundwater flow models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to evaluate the predictive performance of NMR-derived hydraulic conductivity (K) models and assess how different spatial interpolation and upscaling approaches influence flow and drawdown predictions in a highly heterogeneous aquifer system.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Natural and anthropogenic drivers of the water table dynamics in a riparian fen peatland
This publication, co-authored by Adrien Renaud, Claude Mügler, Véronique Durand, and Marc Pessel, which examines the natural and anthropogenic drivers of water table dynamics in a riparian fen peatland along the Essonne River in France. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to couple surface and subsurface hydrology, providing new insights into how precipitation seasonality, vegetation activity, and river regulation influence peatland water levels.
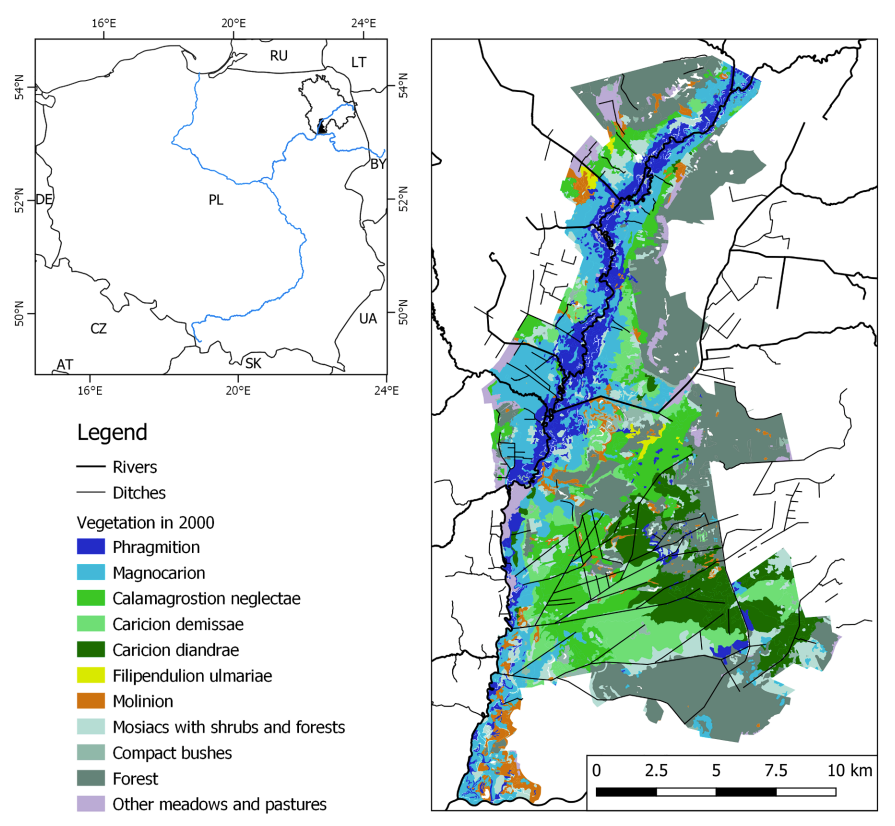
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Using water sources extent during inundation as a reliable predictor for vegetation zonation in a natural wetland floodplain
We’re pleased to highlight this publication, co-authored by Tomasz Berezowski and Martin Wassen, which investigates how the extent of water sources during inundation can be used as reliable predictors of vegetation zonation in wetland floodplains. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) together with the Hydraulic Mixing-Cell (HMC) method to address long-standing challenges in modelling vegetation dynamics by explicitly accounting for the spatial distribution of different water sources during floods.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Groundwater flow and age in topography-driven groundwater flow systems with geological barriers
The research examines how groundwater age and flow systems are influenced by topography and geological barriers, using numerical simulations to clarify the interaction between surface-driven flow and subsurface heterogeneity. Traditional models of topography-driven flow often assume homogeneous geologic conditions, which can obscure the role of stratigraphic variations in shaping groundwater movement and age distribution. This study offers a detailed exploration of how structural barriers— such as low-permeability formations— interrupt or redirect groundwater pathways and affect the spatial and temporal distribution of groundwater age.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – External and internal drivers behind the formation, vegetation succession, and carbon balance of a subarctic fen margin
In this research publication, researchers investigated the formation, vegetation succession, and carbon balance of peatland margins in Finnish Lapland. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) alongside paleoecological records and remote sensing to address long-standing challenges in understanding how new peatland areas initiate, expand, and influence climate through carbon cycling.

Staff Research Highlight - Improving precision in regional scale numerical simulations of groundwater flow into underground openings
The study presents a novel numerical framework to improve the accuracy of regional-scale groundwater flow simulations into underground openings, such as tunnels and deep geological repositories. Traditionally, simulating groundwater inflows into engineered underground structures has involved significant simplifications, often treating tunnels as drain features or imposing boundary conditions that fail to fully capture the physical behavior of fluid flow around these voids. This research addresses those limitations by introducing a new numerical boundary condition to simulate groundwater flow into underground openings more accurately.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Model simplification to simulate groundwater recharge from a perched gravel-bed river
This publication co-authored by Antoine Di Ciacca, Scott Wilson, Patrick Durney, Guglielmo Stecca, and Thomas Wöhling, investigates model simplification strategies to simulate groundwater recharge from perched gravel-bed rivers. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) as a fully integrated 3D surface–subsurface model, alongside 2D cross-sectional and 1D analytical models, to address long-standing challenges in representing river–aquifer interactions while reducing computational demands.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Is the Water Balance of Your Waste Rock Pile Reliable? A framework for Improving Assessment of Water Inputs and Outputs for a Typical Storage Facility
This research focuses on understanding the dynamics of topography-driven groundwater flow systems using fully-coupled surface–subsurface hydrologic modelling. This study addresses long-standing challenges in representing nested flow systems by simulating interactions between climate, topography, and groundwater without relying on potentially unrealistic, static boundary conditions.

Staff Research Highlight - Quantifying the potential of using Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) soil moisture variability to predict subsurface water dynamics
Aquanty staff investigate the potential for using near-surface soil moisture measurements from the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite to predict subsurface soil moisture and groundwater storage dynamics. This research offers valuable insights into how satellite-based soil moisture data can inform large-scale hydrological modelling and support more effective water resource management.
