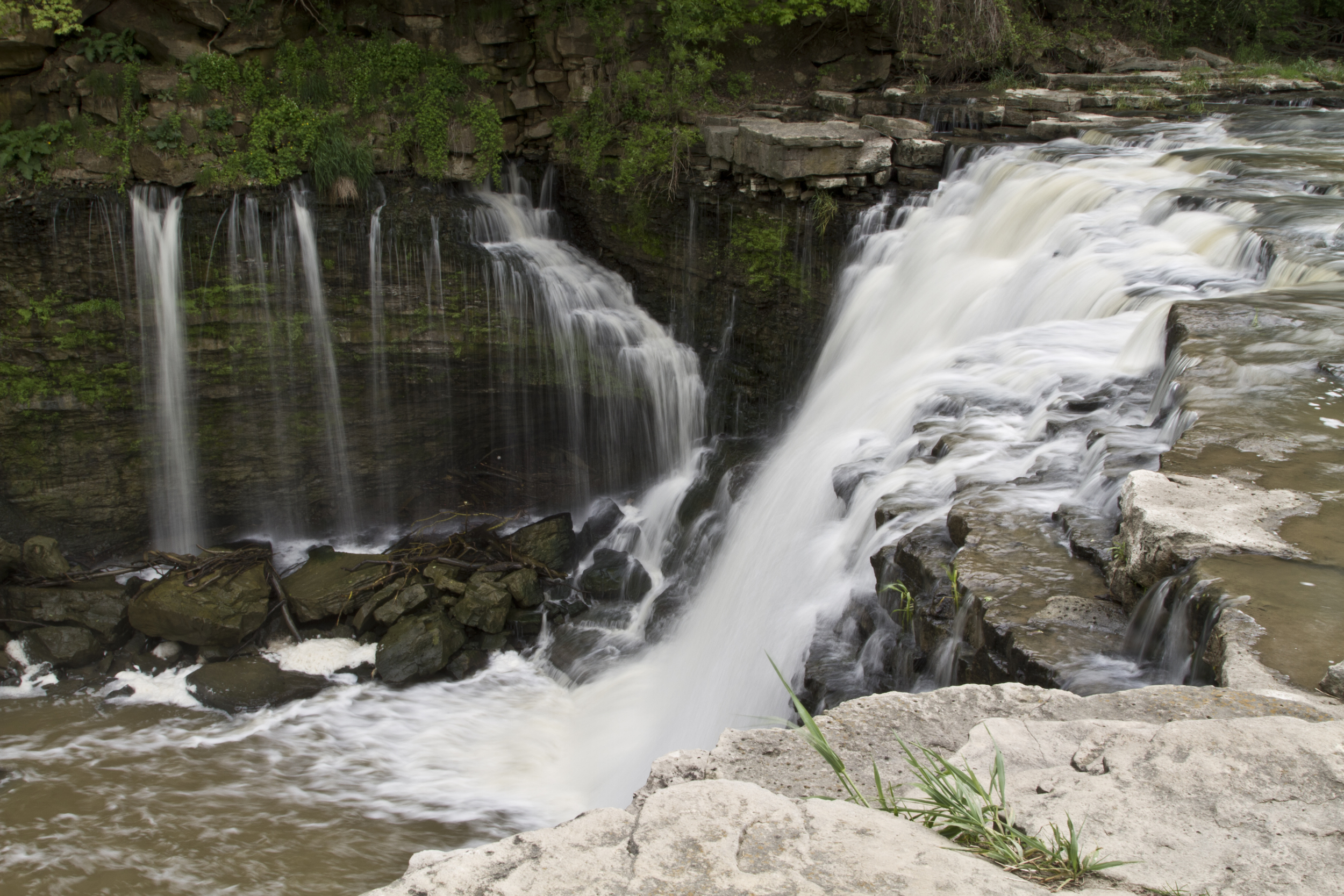


Assign Multiple Observation Points Based on Depth from Ground Surface
This post describes how to use six new commands introduced in the June 2022 release (Revision 2409) of HydroGeoSphere that simplify the definition of observation points in your models. These commands allow you to assign observation points based on absolute elevations or depth from ground surface, making it easier to work with field data and reducing manual input. Conceptually, these commands streamline the process by allowing direct placement of observation points relative to known reference levels. We find these commands particularly useful for efficiently defining observation networks and improving model setup workflows.




HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Sources of surface water in space and time: Identification of delivery processes and geographical sources with hydraulic mixing-cell modeling
The paper highlighted this week presents a very interesting post-processing method for HydroGeoSphere models. The results of the HGS model were used as input into the hydraulic mixing-cell (HMC) approach which enables tracking and delineation of the mixing of predefined initial water sources at any location and at any time based on information from the hydraulic flow solution

'use tabulated unsaturated functions'
This post describes how to use the use tabulated unsaturated functions command, introduced in the May 2022 release (Revision 2397) of HydroGeoSphere, to streamline the implementation of tabular constitutive relationships for unsaturated flow. By automating the process of generating and applying unsaturated tables, this command reduces manual steps and can improve model runtimes. However, in some cases, using unsaturated tables may introduce additional computational overhead. We find this command particularly useful for users working with van Genuchten or Brooks-Corey functions who want to optimize performance while maintaining accuracy.



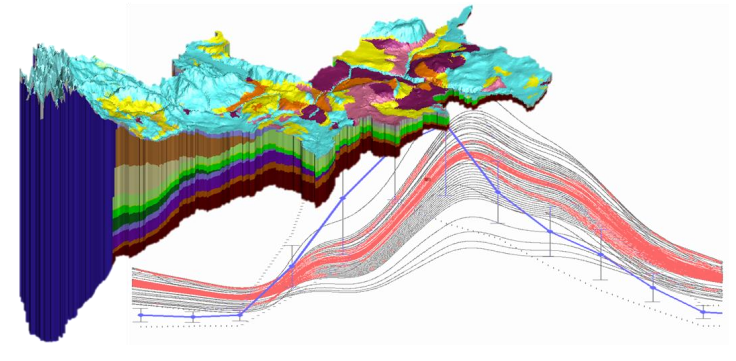
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Transit-Time and Temperature Control the Spatial Patterns of Aerobic Respiration and Denitrification in the Riparian Zone
The paper highlighted this week introduces a novel method of implementing temperature-dependent reactions in a HydroGeoSphere solute transport model by pairing a Lagrangian flow path-reaction model to the results of a 2nd order Runge-Kutta particle tracking analysis.
