

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Impact of Baseflow on Fish Community in the Ungcheon Stream, Korea
In this research highlight, researchers have explored how baseflow influences fish habitats in the Ungcheon stream, located downstream of the Boryeong Dam in Korea.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – HGS-PDAF (version 1.0): a modular data assimilation framework for an integrated surface and subsurface hydrological model
In their recent publication, Qi Tang and her team present an advancement in hydrological modelling: HGS-PDAF (version 1.0). This modular data assimilation framework is tailored specifically for integrated surface and subsurface hydrological modelling, offering a powerful tool for understanding and managing water resources in a changing environment.

NEW version of HGS (HGS PREMIUM JUNE 2024 (REVISION 2699)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2699 (June 2024) is now available for download.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Same soil, different climate: Crop model intercomparison on translocated lysimeters
In this research highlight, researchers explored the dynamics of crop modelling across diverse climatic conditions using translocated lysimeters. The study investigates how crop models perform when applied to the same soil under different climatic regimes, shedding light on the complex interplay between soil and crop dynamics amidst changing environmental conditions.
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Small-scale topography explains patterns and dynamics of dissolved organic carbon exports from the riparian zone of a temperate, forested catchment
Examining the intricate dynamics of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) exports from riparian zones (RZs), a recent study conducted by a team of researchers highlights the predominant controls governing DOC export.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Hydraulic Tomography Estimates Improved by Zonal Information From the Clustering of Geophysical Survey Data
Exploring innovative methods in groundwater characterization, Chenxi Wang and Walter A. Illman present a study on improving Hydraulic Tomography (HT) estimates through the integration of geophysical survey data. Hydraulic tomography offers valuable insights into subsurface heterogeneity by analyzing multiple pumping tests. However, challenges arise when insufficient observations lead to smooth or inaccurate tomograms. In this study, Wang and Illman investigate the integration of geophysical survey data into HT analysis to address this issue.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Heat Tracing in a Fractured Aquifer with Injection of Hot and Cold Water
In this comprehensive study, researchers explore the application of heat as a tracer in fractured porous aquifers, offering new perspectives on groundwater flow and transport dynamics. The research paper investigates the use of hot (50 °C) and cold (10 °C) water injections in a weathered and fractured granite aquifer, where the natural background temperature is 30 °C. This study relies on a number of advanced HGS capabilities including density-dependent geothermal energy transport, fracture flow and time-varying material properties.

"HydroSphereAI: Machine Learning for Flood and Drought Forecasting" - Aquanty Webinar
Aquanty has developed a new machine-learning model that can produce highly accurate streamflow forecasts hours or days into the future. We are currently working on integrating these new capabilities into our suite of web-based water decision support tools. As one of the only companies in Canada currently doing this kind of forecasting, we are well positioned to meet a growing need for advanced forecasting tools. ML-based streamflow forecasts are currently available for a small selection of watersheds in southwestern Ontario through Aquanty’s HGSRT web platform.
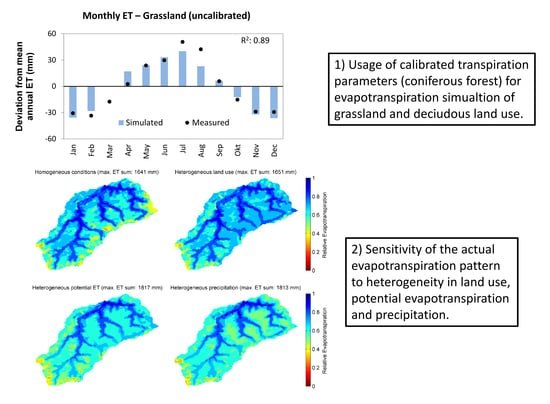
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Using High-Resolution Data to Test Parameter Sensitivity of the Distributed Hydrological Model HydroGeoSphere
By integrating HydroGeoSphere in this study, the researchers demonstrate its versatility in accommodating high-resolution data and conducting sensitivity analyses across different spatial scales. Precipitation emerges as the most sensitive input data, significantly influencing total runoff and peak flow rates. Additionally, the study highlights the importance of spatially distributed land use parameterization in accurately simulating evapotranspiration components and patterns.
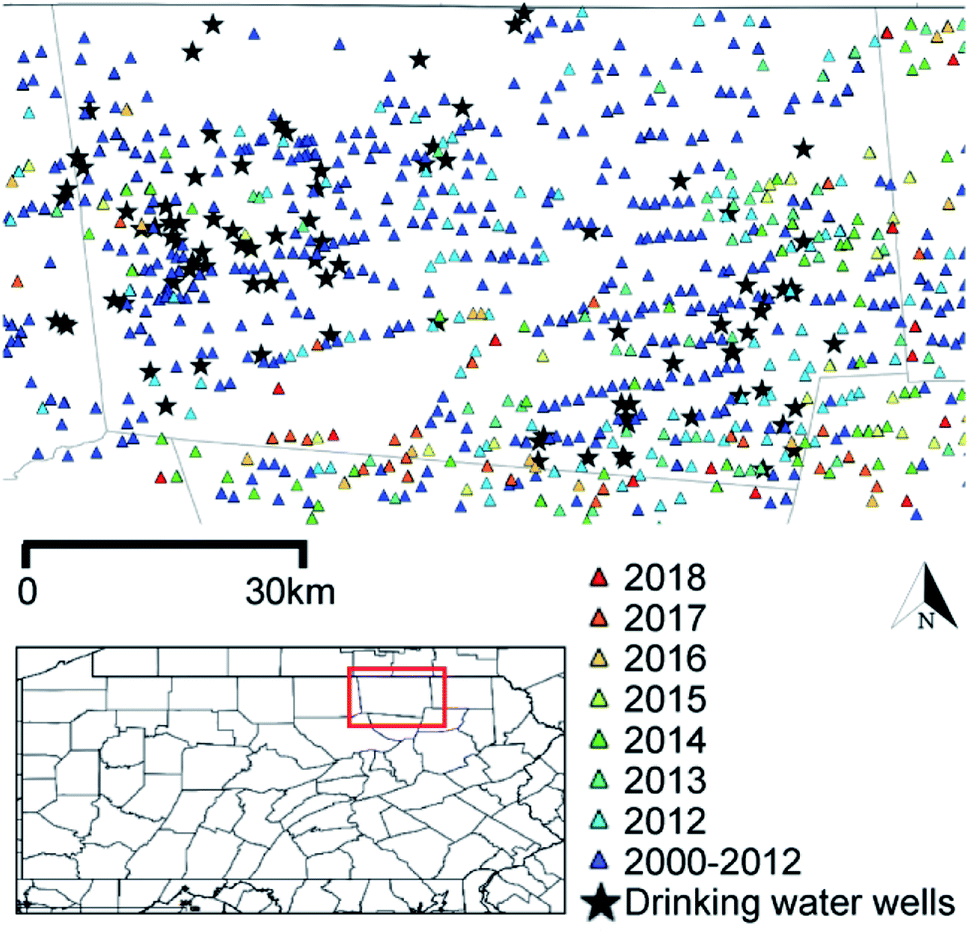
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Groundwaters in Northeastern Pennsylvania near intense hydraulic fracturing activities exhibit few organic chemical impacts
In this comprehensive study, researchers investigated the potential impact of hydraulic fracturing activities on groundwater quality in Northeastern Pennsylvania, using a HydroGeoSphere model of a region with thirty gas-well pads. Modelling results suggest a low probability of systematic groundwater organic contamination in the region.
