

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Saltwater Intrusion Into a Confined Island Aquifer Driven by Erosion, Changing Recharge, Sea-Level Rise, and Coastal Flooding
This research sheds light on the complex interactions between storm surges, reduced recharge, high erosion rates, and sea-level rise on the hydrological balance of Prince Edward Island. By leveraging the advanced capabilities of HGS, the researchers were able to test impact that climate change and future trends in coastal hydrology will have on the islands groundwater quality and the movement on the saltwater wedge underlying PEI.

HydroGeoSphere Research Paper wins Water Resources Research Editors’ Choice Award
We’d like to highlight a terrific achievement in the HydroGeoSphere user community, and send a hearty congratulations to Dr. James Thornton and his research team for winning the 2022 Editors’ Choice Award from the Water Resources Research journal.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Simulating the recession dynamics of Arctic catchments in the context of a thawing permafrost
In a recent study, researchers have made significant strides in understanding how climate warming is altering the Arctic's hydrological dynamics. The study delves into the complex relationship between permafrost thaw and groundwater flow. Traditionally, Arctic hydrology has been conceptualized as a local system, confined by the frozen ground. However, as the climate warms, permafrost begins to thaw, transitioning this system into a more interconnected network of regional aquifers. This transformation is crucial, as it alters the fundamental dynamics of water movement and storage in the Arctic.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Understanding the vulnerability of surface–groundwater interactions to climate change: insights from a Bavarian Forest headwater catchment
This study used HydroGeoSphere to evaluate the impact of climate change on streamflow and water availability within a small forested catchment in South-East Germany. Climate forecasts in the region predict a significant decrease in precipitation over the coming decades. Based on integrated hydrologic modelling of the catchment, this forecasted decline in precipitation combined with a relatively steady rate of evapotranspiration (compared to the historical period) will result in prolonged drought conditions, which in turn will result in declining groundwater levels, decreased baseflow to the upstream reaches of the stream network.
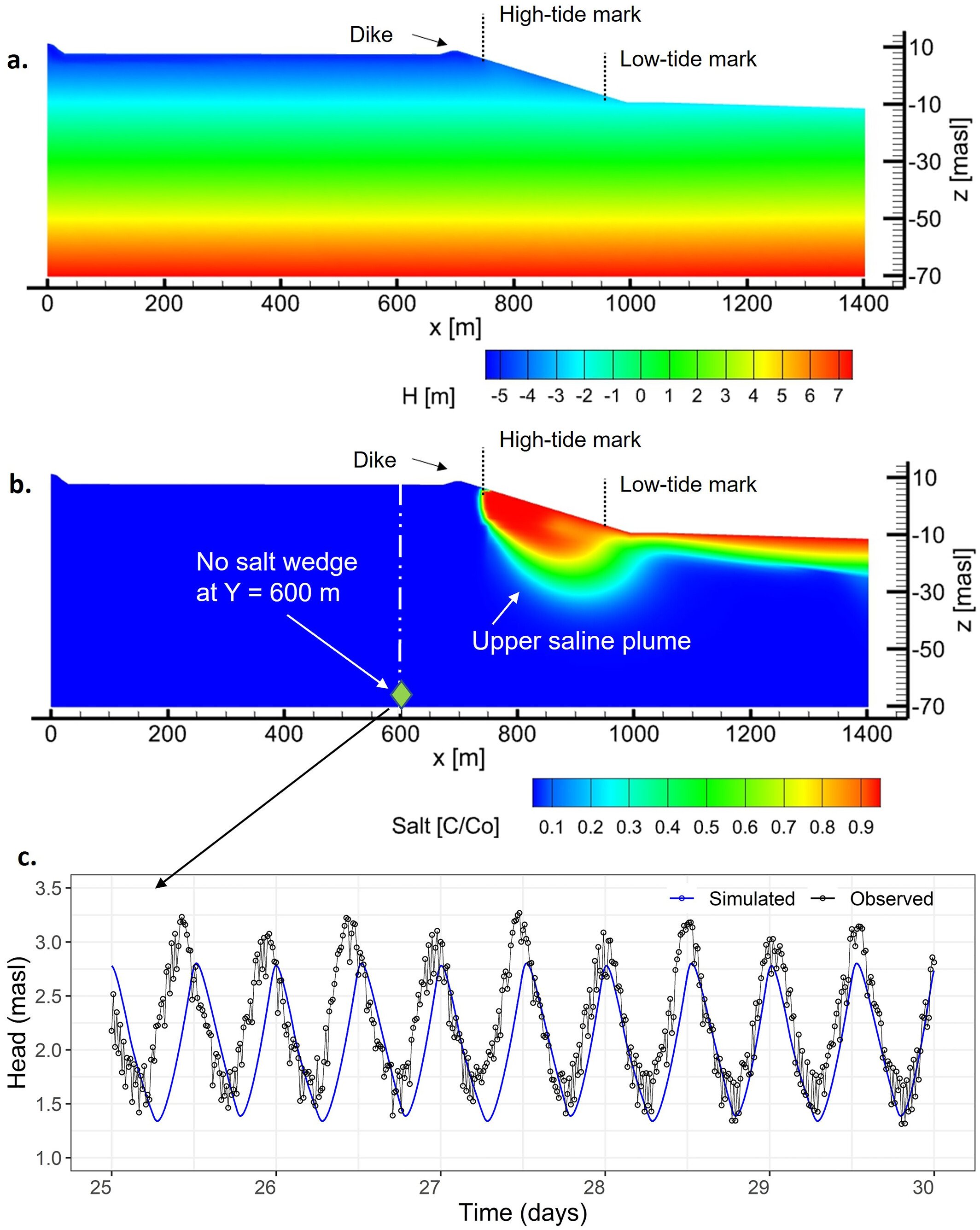
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Mega-Tidal and Surface Flooding Controls on Coastal Groundwater and Saltwater Intrusion Within Agricultural Dikelands
The study highlighted here makes full use of the density dependent flow modelling capabilities of HydroGeoSphere to investigate the impacts of climate change on groundwater-ocean interactions, and how sea-level rise, tides and storm-surges impact the long-term position of an upper saline plume in a coastal agricultural dikeland in Nova Scotia, Canada.


HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Groundwater flow reversal between small water bodies and their adjoining aquifers: A numerical experiment
This recent study uses HydroGeoSphere to investigate groundwater-surface water interactions within “kettle holes” - post glacial landscape features prevalent across Northern Europe and Northern America. These kettle holes are quite similar to lakes, but their smaller size makes them prone to drying out, which results in very dynamic and variable groundwater-surface water interactions, sometimes being subject to groundwater flow reversal between a kettle hole and the adjacent aquifer.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Evaluation of Hydraulic Conductivity Estimates from Various Approaches with Groundwater Flow Models
Over several decades a wide variety of techniques have been used to estimate the hydraulic flow properties of the subsurface. Here the authors have produced heterogeneous hydraulic conductivity (K) distributions at a heavily instrumented research site using 6 distinct techniques (slight variations in some tests resulted in 9 distinct K distributions):.

HydroGeoSphere Research Highlight - "Lateral and vertical saltwater intrusion into a coastal aquifer"
Climate change is projected to substantially increase the global mean sea level, which will adversely impact coastal communities worldwide.
