

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Heat Tracing in a Fractured Aquifer with Injection of Hot and Cold Water
In this comprehensive study, researchers explore the application of heat as a tracer in fractured porous aquifers, offering new perspectives on groundwater flow and transport dynamics. The research paper investigates the use of hot (50 °C) and cold (10 °C) water injections in a weathered and fractured granite aquifer, where the natural background temperature is 30 °C. This study relies on a number of advanced HGS capabilities including density-dependent geothermal energy transport, fracture flow and time-varying material properties.

"Machine Learning for Flood and Drought Forecasting" - Aquanty Webinar
Aquanty has developed a new machine-learning model that can produce highly accurate streamflow forecasts hours or days into the future. We are currently working on integrating these new capabilities into our suite of web-based water decision support tools. As one of the only companies in Canada currently doing this kind of forecasting, we are well positioned to meet a growing need for advanced forecasting tools. ML-based streamflow forecasts are currently available for a small selection of watersheds in southwestern Ontario through Aquanty’s HGSRT web platform.
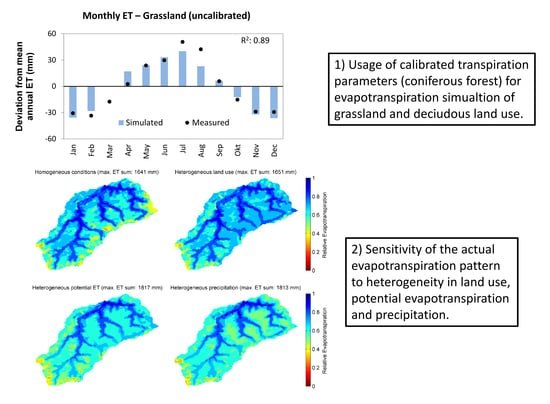
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Using High-Resolution Data to Test Parameter Sensitivity of the Distributed Hydrological Model HydroGeoSphere
By integrating HydroGeoSphere in this study, the researchers demonstrate its versatility in accommodating high-resolution data and conducting sensitivity analyses across different spatial scales. Precipitation emerges as the most sensitive input data, significantly influencing total runoff and peak flow rates. Additionally, the study highlights the importance of spatially distributed land use parameterization in accurately simulating evapotranspiration components and patterns.
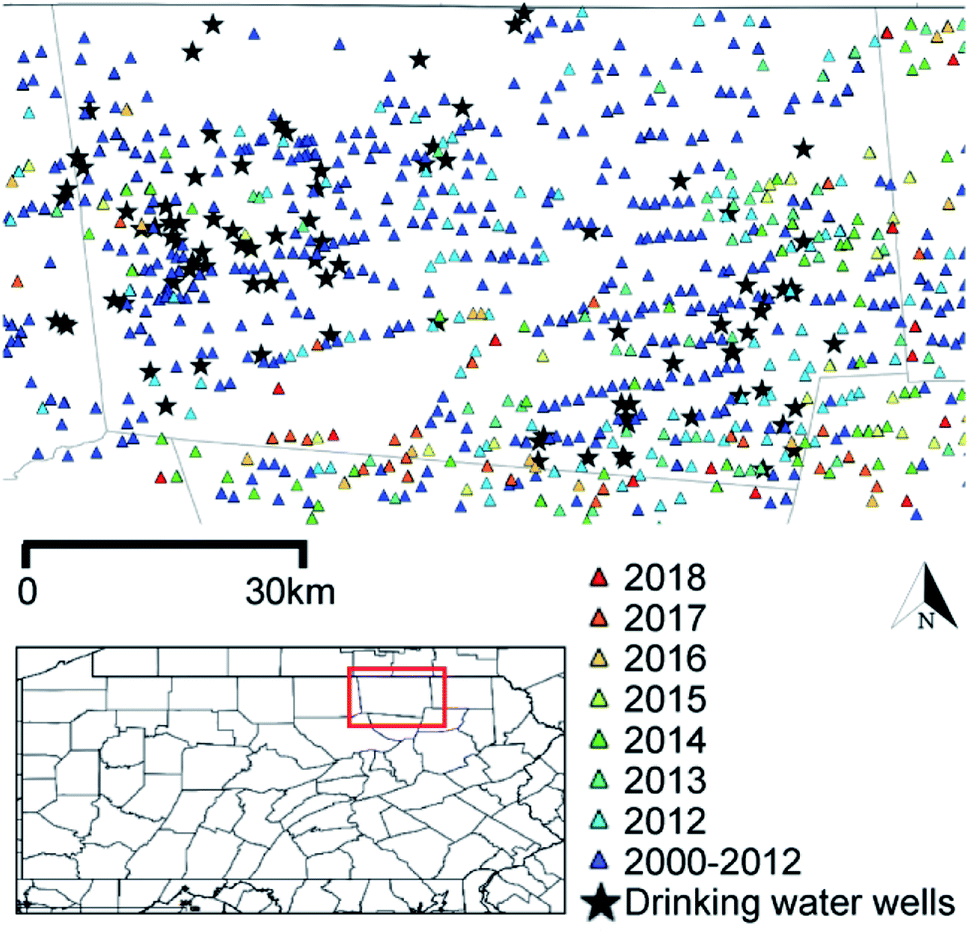
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Groundwaters in Northeastern Pennsylvania near intense hydraulic fracturing activities exhibit few organic chemical impacts
In this comprehensive study, researchers investigated the potential impact of hydraulic fracturing activities on groundwater quality in Northeastern Pennsylvania, using a HydroGeoSphere model of a region with thirty gas-well pads. Modelling results suggest a low probability of systematic groundwater organic contamination in the region.

NEW version of HGS (April 2024 - Revision 2674)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2674 (April 2024) is now available for download.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – How Does Topography Control Topography-Driven Groundwater Flow?
In a study led by Xiaolang Zhang, Jiu Jimmy Jiao, Wensi Guo, researchers have comprehensively explored the mechanisms governing topography-driven groundwater flow. Their research showcases the complexities between varying rainfall patterns, topographic features, and groundwater flow dynamics, offering invaluable insights into hydrological processes.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Comparing alternative conceptual models for tile drains and soil heterogeneity for the simulation of tile drainage in agricultural catchments
This research highlight explores tile drainage systems within agricultural catchments, with the goal of refining hydrological modeling methodologies. The study explores the impact of soil heterogeneity on model simulations, revealing its significance at smaller scales. Overall, offering valuable insights into improving the representation of tile drainage in hydrological models, crucial for sustainable water management in agricultural landscapes.

Ontario Water Consortium - WIG Project Highlight: Using machine learning to make flood forecasts less wishy-washy
The Ontario Water Consortium has written an excellent article which reviews Aquanty’s latest technology driven initiative that can be used to manage water resources. With support from the Ontario Water Consortium’s Water Industry Growth Program, Aquanty is making machine-learning (i.e. artificial intelligence) driven real-time flood forecasting a reality.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – The coastal aquifer recovery subject to storm surge: Effects of connected heterogeneity, physical barrier and surge frequency
This research analyzes the combined effects of connected heterogeneity, physical barriers, and surge frequency on coastal aquifer recovery. Using HydroGeoSphere (HGS), Aquanty’s sophisticated modeling platform known for its ability to simulate coupled surface water-groundwater interactions, the team investigated a series of modeling cases in heterogeneous and equivalent homogeneous aquifers.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Fractal Behaviors of Hydraulic Head and Surface Runoff of the Nested Groundwater Flow Systems in Response to Rainfall Fluctuations
In this paper the authors have undertaken a comprehensive investigation into the behavior of nested groundwater flow systems (NGFS) in response to rainfall fluctuations and their influence on surface runoff. Through the utilization of a fully coupled variably saturated groundwater-surface water model alongside spectral analysis, the team delves into the fractal characteristics of hydraulic head and surface runoff across different scenarios.
